AI Governance Framework
An AI governance framework is a structured set of policies, processes, and standards designed to ensure that AI systems are developed, deployed, and managed responsibly. These frameworks provide guidelines for ethical decision-making, transparency, accountability, and compliance with regulations throughout the AI lifecycle.
By implementing an AI governance framework, organizations can mitigate risks and impacts, foster trust, and align AI systems with societal and legal expectations.
Why Are AI Governance Frameworks Actionable?
AI is increasingly influencing critical areas like finance, healthcare, and law enforcement. In the absence of concrete governance structures, AI systems can introduce ethical, legal, and societal challenges. A well-designed AI governance structure helps organizations:
-
Mitigate Risks: Address biases, ethical concerns, and unintended consequences in AI systems.
-
Ensure Compliance: Adhere to global AI compliance frameworks and regulatory standards.
-
Build Trust: Foster transparency and accountability in decision-making processes.
-
Promote Innovation: Encourage responsible use of AI while balancing creativity and safeguards.
-
Change Management: Continuously adapt AI governance to keep up with evolving technologies and compliance requirements.
Key Components of an AI Governance Framework
A comprehensive AI governance framework typically includes the following elements:
1. Ethical Guidelines
Organizationally-specific policies that define acceptable AI practices, focusing on fairness, transparency, and user privacy.
2. AI Governance Standards
Adherence to global and industry-specific regulations, ensuring compliance with laws like GDPR and the EU AI Act.
3. Accountability Mechanisms
Defining roles and responsibilities for teams involved in AI development and deployment.
4. Transparency and Explainability
Guidelines to ensure AI systems provide clear, interpretable, and traceable outcomes.
5. Machine Learning Model Governance
Processes to oversee the lifecycle of machine learning models, including training, testing, deployment, and continuous monitoring.
6. Use-Case Specificity
Tailoring governance frameworks to specific AI use-cases to ensure relevance and precision in addressing unique risks and requirements.
7. Risk Management
Proactive strategies to identify and address risks, such as bias, security vulnerabilities, and ethical violations.
AI Governance Models
Different AI governance models can be applied depending on an organization’s goals and requirements:
-
A Layered Model for AI Governance: This model segments governance into multiple layers, such as data governance, algorithm governance, and decision governance, ensuring comprehensive oversight at every stage.
-
Policy-Driven AI Governance: Emphasizes the use of targeted AI policiesto establish clear rules and ethical principles for AI use.
-
AI Model Governance Framework: Focuses specifically on managing the performance, accountability, and explainability of AI models.
How to Build an Effective AI Governance Framework
Organizations can establish a robust AI governance structure by following these steps:
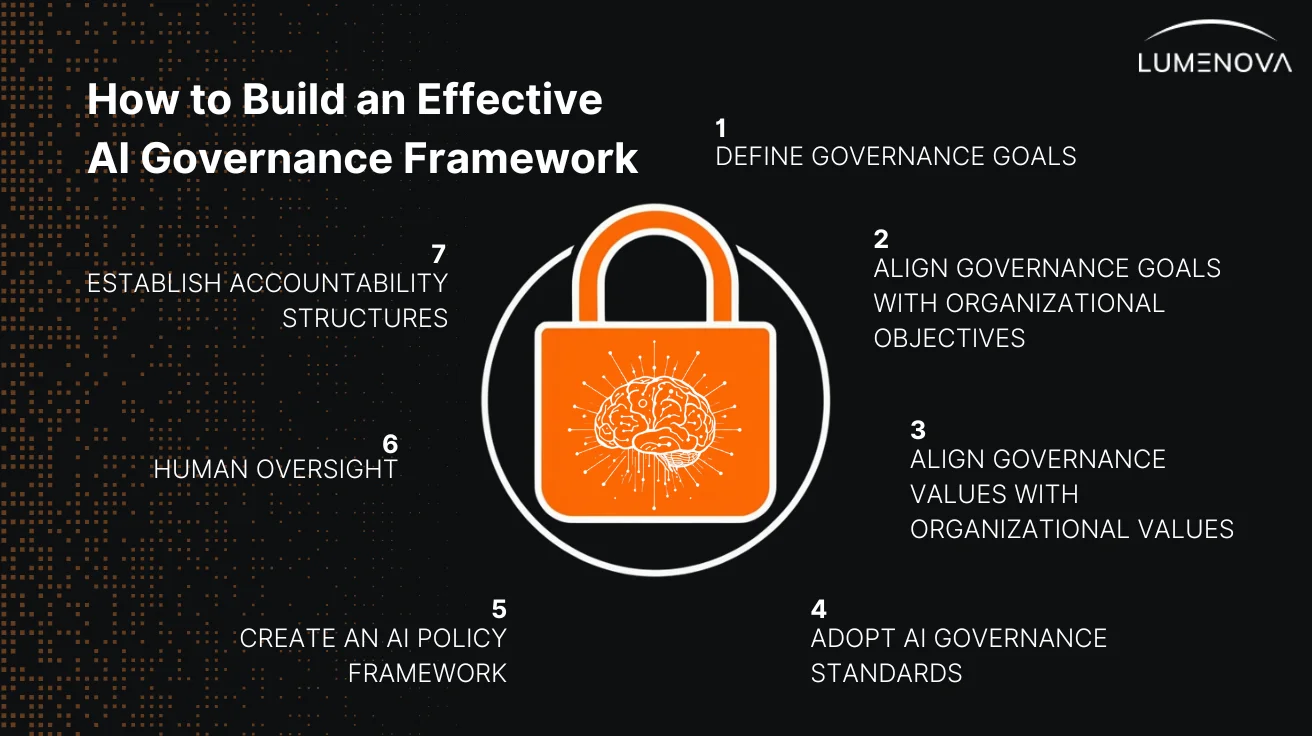
1. Define Governance Goals
The first step in creating an AI governance framework is to define the core goals of your governance structure. What do you want to achieve? Are you focused on regulatory compliance, promoting fairness, or ensuring transparency in AI decision-making processes? Setting clear and specific goals at this stage ensures that your AI governance framework will be purpose-driven and focused on achieving measurable outcomes. This is essential for both mitigating risks and fostering trust in AI systems.
2. Align Governance Goals with Organizational Values and Objectives
AI governance isn’t generic or one-size-fits-all. It should always tie back to the bigger picture of your business’ values and objectives. How does this framework support your company’s mission? Does it enhance efficiency while balancing employee automation concerns? Does it support innovation without compromising sustainability initiatives? Does is improve customer satisfaction without revealing sensitive data characteristics? Mapping AI governance onto organizational values and objectives helps ensure that AI initiatives won’t just work in theory but in practice, throughout real-world deployment contexts.
3. Adopt AI Governance Standards
Incorporating globally recognized AI governance standards, such as the EU AI Act, GDPR, and ISO regulations, is crucial, even in cases where commitments to these standards might be voluntary. Such standards ensure your AI systems align with ethical and legal best practices, minimizing data privacy, ethics, and transparency risks.
4. Create AI Policies
To support your governance structure, develop comprehensive AI policies that define ethical AI practices, risk management protocols, and decision-making processes. Policies should provide clear guidelines on how AI will be developed, implemented, and monitored within your organization. This framework should also include AI use standards, setting operational boundaries for AI applications to enablecompliance and ethical use.
5. Human Oversight
AI systems cannot operate in a vacuum. Even with the most sophisticated algorithms, human oversight is critical. Implementing regular monitoring and auditing procedures allows organizations to assess AI system performance, identify potential risks and impacts, and ensure compliance with established guidelines. Human oversight is also necessary for transparency and fairness, informing the development of safeguards against biased outcomes or unintended consequences. Overall, ongoing oversight ensures that AI systems remain aligned with your governance goals throughout their lifecycle.
6. Establish Accountability Structures
Clear accountability structures are essential for effective AI governance. Assign roles and responsibilities to specific teams and individuals to manage and oversee AI systems. This supports a direct line of accountability regarding AI risks and impacts. Teams should be empowered to make decisions, address issues promptly, and enforce governance policies to maintain the integrity of AI systems.
Examples of AI Governance in Action
- Finance: Machine learning model governance ensures that AI-powered credit scoring systems comply with fairness and transparency standards.
- Healthcare: AI governance frameworks are used to validate medical AI models for accuracy and patient safety.
- Manufacturing: AI compliance frameworks guide predictive maintenance systems to prevent equipment failures and maintain worker safety.
- Retail: Organizations implement governance models to ensure recommendation algorithms align with privacy and ethical standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
An AI governance framework is a set of guidelines, processes, and policies that ensure AI systems are ethical, transparent, accountable, and compliant with regulations.
Machine learning model governance ensures that AI models perform accurately, align with ethical standards, and remain compliant with evolving regulations.
AI governance standards are globally recognized benchmarks and best practices that guide the responsible development and deployment of AI systems.
A layered model for AI governance segments governance responsibilities into layers, such as data handling, algorithm monitoring, and decision accountability, to ensure comprehensive oversight.
AI policies provide clear, actionable rules and ethical guidelines for the development and use of AI. These policies are built upon the foundation laid by the AI governance framework and are specifically tailored to meet organizational goals and societal expectations.