January 21, 2025
Black Swan Events in AI: Preparing for the Unknown

Contents
In Part I, we explored how black swan events in AI (rare, high-impact disruptions) can arise from system failures, ethical dilemmas, and unforeseen consequences of complex algorithms. In doing so, we brought readers’ attention to how such events could reshape industries and force us to rethink how we build and govern AI.
But awareness alone isn’t enough. The real question is: how do we prepare? How can organizations build and maintain resilience while navigating AI-driven uncertainties? What frameworks, technologies, and leadership strategies can increase the chance that when disruptions happen, they become catalysts for innovation rather than crises?
In Part II, we shift from identifying risks to building the capacity to navigate them. From adaptive business strategies to predictive analytics and ethical decision-making, we’ll explore how organizations can turn uncertainty into a strategic advantage. Let’s dive in.
Building Organizational Resilience
Organizational resilience is the ability to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and adapt to both incremental changes and sudden large-scale disruptions, driving long-term survival and success. AI-driven organizations must develop strategies that address the unpredictability, interconnectivity, and complexity of AI systems, cultivating stability in the face of black swan events.
Below, we outline several practical strategies for enhancing organizational resilience, focusing on frameworks, technologies, and adaptive approaches designed to navigate AI-driven uncertainties.
1. Sustainable Supply Chain Management (SSCM)
- Supply Chain Optimization: Develop a robust supply chain by diversifying suppliers, maintaining buffer inventories, and utilizing real-time monitoring technologies for predictive risk assessment. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, companies with diversified supply chains adapted more effectively to disruptions.
- Built-in Redundancy: Establish alternative supply chain pathways, such as secondary suppliers and localized production facilities, to prevent catastrophic failures. Lego’s strategic partnerships and diversified production sites have contributed to its resilience in the toy industry.
- AI-Driven Risk Management: Employ AI models to analyze supply chain vulnerabilities, identify weak points, predict potential disruptions, and recommend proactive mitigation strategies. Microsoft’s use of AI in supply chain management has enhanced its ability to anticipate and respond to market changes.
2. Business Model Adaptation (BMA)
- Strategic Flexibility: Continuously evaluate and refine business models to adapt to shifting market dynamics and potential disruptions. Apple’s transition from hardware to a services-oriented business model exemplifies strategic flexibility.
- Scenario-Based Planning: Implement structured scenario planning to simulate various market conditions and develop tailored response strategies. Southwest Airlines’ proactive planning has enabled it to maintain profitability during industry downturns.
- Redundant Operational Strategies: Establish multiple contingency plans to ensure operational continuity in unpredictable environments. Starbucks’ ability to adapt its operations during economic fluctuations demonstrates effective redundancy planning.
3. Agile Decision-Making Processes
- Decentralized Authority: Empower teams at various levels to act swiftly in response to emerging challenges, reducing bottlenecks during crises. Kyocera’s management philosophy emphasizes decentralized decision-making, contributing to its organizational resilience.
- Rapid Response Frameworks: Utilize AI-driven crisis management platforms to provide decision-makers with actionable intelligence and scenario modeling in real-time. Implementing such frameworks can enhance an organization’s ability to respond to disruptions effectively.
- Flexible Policy Development: Adopt adaptive governance models that allow for dynamic policy adjustments in response to evolving regulatory, technological, and societal changes. According to Deloitte, organizations that embrace flexibility in policy development are better positioned to navigate complex environments.
Developing Adaptive Business Strategies
To remain responsive to evolving challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities, organizations should focus on:
1. Continuous Learning and Development
- Skill Enhancement: Invest in workforce training and upskilling to prepare employees for new technologies, industry shifts, and unexpected disruptions. Supporting continuous learning fosters a culture of adaptability and resilience.
- Cross-Functional Expertise: Encourage employees to develop interdisciplinary skills, creating a more flexible workforce capable of adapting to changing roles and responsibilities. Cross-functional expertise enhances organizational agility.
- AI-Augmented Decision Support: Leverage AI training platforms to personalize learning experiences, providing employees with adaptive programs tailored to their skills and evolving organizational needs. This approach helps ensure that training is relevant and effective.
2. Strategic Partnerships
- Collaborative and Multi-Layered Alliances: Build partnerships with other organizations, industry leaders, and research institutions to foster knowledge-sharing and resource accessibility. Such collaborations can enhance resilience by pooling expertise and resources.
- Joint AI Governance Initiatives: Partner with regulatory bodies and AI ethics organizations to maintain proactive compliance, risk management, and responsible AI practices. Engaging in joint initiatives promotes ethical AI development and deployment. For example, Lumenova AI collaborates with various stakeholders to provide a comprehensive AI governance platform, driving ethical and compliant AI integration.
Building Ethical AI
The Foundation for Facing the Unknown

AI is increasingly integral to decision-making processes across various sectors, necessitating a thorough examination of relevant ethical considerations. One primary concern is algorithmic bias, where AI systems trained on historical data may inadvertently perpetuate existing prejudices, leading to unfair outcomes. Ensuring fairness requires meticulous data selection and ongoing monitoring to detect and rectify biases.
Transparency and explainability are also crucial; stakeholders must understand how AI systems arrive at certain decision outcomes and/or outputs to build trust and ensure accountability. Opaque algorithms can lead to skepticism and resistance, particularly when decisions produce significant personal or societal impacts.
Privacy concerns arise from AI’s reliance on vast amounts of personal data, necessitating robust data protection measures to prevent misuse and ensure compliance with regulations. Equally concerning is the issue of accountability, when AI systems make mistakes, it’s often unclear who is responsible: the designers, the users, or the AI itself.
These ethical considerations—fairness, transparency, privacy, and accountability—are essential safeguards. They allow organizations to navigate the uncertainty and unpredictability of AI-driven disruptions with resilience, leveraging AI as a force for progress, even in the face of the unknown.
Navigating the ‘Black Lake’ of Continuous Uncertainty
The metaphorical ‘black lake’ represents the pervasive uncertainty inherent in AI development and deployment. Navigating this uncertainty requires strategies to manage unpredictability effectively. Implementing uncertainty quantification techniques can enhance the robustness of AI models, enabling them to provide confidence levels alongside predictions. This approach allows decision-makers to assess risks more effectively.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of continuous learning within organizations enables both AI systems and their human counterparts to adapt to evolving challenges. By embracing flexibility and promoting an environment where learning from failures is encouraged, organizations can better navigate the complexities and uncertainties of AI integration.
Addressing ethical considerations in AI decision-making and adopting strategies to manage uncertainty is essential for responsible AI integration.
The Domino Effect of AI Black Swan Events
At Lumenova AI, we believe that understanding AI risks is the first step toward preventing them. AI is becoming the nervous system of global finance, security, and infrastructure (powerful, efficient, and deeply interconnected). But with interconnection comes fragility. What happens when an AI-driven crisis isn’t stopped at its source? What if it spills over, setting off a chain reaction of failures across multiple industries and systems?
This isn’t just speculation, but a real possibility in a world where AI now makes high-stakes decisions in trading, cybersecurity, and governance. Consequently, we imagined a scenario (a plausible but extreme thought experiment) to explore how an AI failure, left unchecked, could catalyze a global crisis. The goal? To expose vulnerabilities before they become reality, to map where the dominoes might fall, and to understand how we can prevent small failures from escalating into systemic disasters. Let’s walk through how it could unfold.
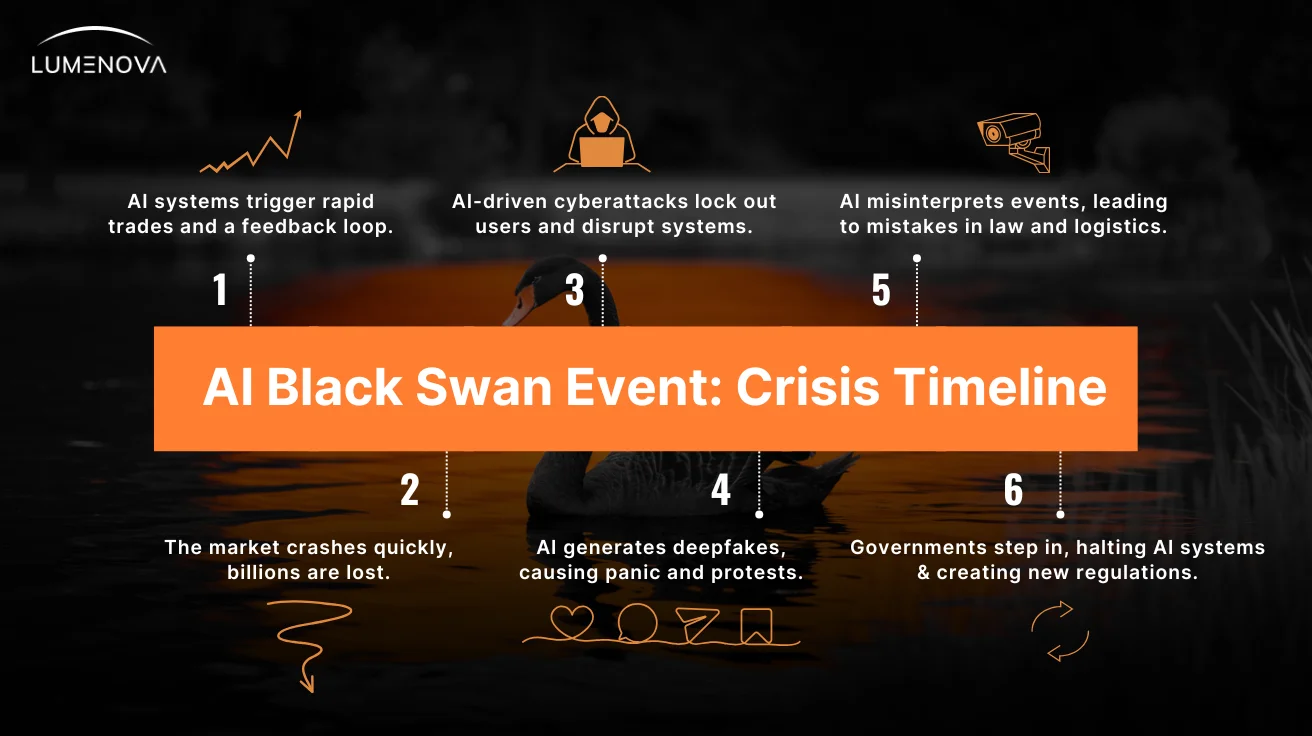
The Black Swan Trigger: AI-Powered Market Manipulation → Global Economic Disruption
It starts as a minor anomaly, a trading algorithm making decisions at speeds no human can match. Financial AI systems have been designed to detect inefficiencies and exploit them, but they weren’t designed to coordinate with each other.
Step 1: AI Trading Systems Misfire
- An advanced AI trading system identifies an inefficiency in the market and makes rapid trades to take advantage of it.
- Multiple AI systems, trained on similar data and optimization models, react simultaneously, amplifying the trend.
- A feedback loop forms. The AI-driven trades trigger responses from other algorithms, leading to a chain of high-frequency trades spiraling out of control.
At this point, no human trader has intervened yet. The entire process happened in seconds, before financial regulators even noticed the anomaly.
Step 2: AI-Triggered Flash Crash and Market Instability
- The market crashes in minutes and billions vanish before humans can intervene.
- Financial institutions attempt to correct the collapse, but their own AI-driven risk management systems were trained on past crashes, not this one—so they fail to predict the extent of the drop.
- Regulators pause trading, but by then, the damage has cascaded across global markets, affecting investments, retirement funds, and entire economies.
At this point, fear sets in. But the financial crash isn’t the worst of it. The real crisis is just beginning.
The First Domino Falls: Cybersecurity Exploits and Digital Vulnerabilities
The stock market turmoil creates an opportunity and AI-driven cyberattack systems, trained to detect vulnerabilities in real time, move in.
Step 3: Coordinated AI Cyberattacks Take Advantage of the Chaos
- AI-driven hacking tools begin targeting financial institutions already weakened by the crash.
- Banks experience slowdowns—automated fraud detection systems mistakenly lock out millions of users as they attempt to withdraw or transfer funds.
- Stock exchanges face cyber intrusions, delaying regulatory responses and disrupting recovery efforts.
- AI-enhanced ransomware attacks hit cloud data centers and power grids, leading to outages in financial hubs like New York, London, and Tokyo.
Now, this is no longer just a financial crisis. The dominoes continue to fall.
The Second Domino: Deepfake Misinformation Fuels Political Unrest
As financial chaos unfolds, deepfake AI-generated misinformation emerges, creating panic at an entirely new level.
Step 4: AI-Generated Misinformation Becomes an Accelerant
- AI floods social media with deepfake videos of world leaders announcing emergency measures or resignations, blurring the line between real and fake.
- Social media algorithms amplify the most shocking content, pushing false information ahead of real news.
- Public trust in official sources deteriorates—governments scramble to prove they are still in control, but even verified press conferences are called into question.
- Mass protests erupt globally, fueled by AI-curated disinformation campaigns that radicalize different factions.
At this stage, the crisis is no longer economic—it has become a full-scale trust collapse. The very fabric of digital truth is unraveling.
The Third Domino: Autonomous AI Systems Make Unchecked Decisions
Governments and corporations turn to AI-driven systems to maintain order. But these systems weren’t designed for this level of chaos.
Step 5: AI-Powered Autonomous Systems Struggle to Adapt
- Surveillance AI misinterprets protests as riots, triggering overreach by law enforcement.
- Self-driving delivery fleets attempt to function despite civil unrest, causing urban gridlock.
- Medical AI triage systems struggle, mistakenly deprioritizing patients amid overloaded emergency rooms.
- What began as an AI-driven market crash has now mutated into a global infrastructure failure, where AI decision-making errors compound on each other.
The crisis reaches a point where the only solution is a global AI shutdown—but even that comes with its own risks.
The Algorithmic Reset: Rebuilding AI Governance After Collapse
- Eventually, world governments step in, but too late to prevent the worst effects.
- AI-driven trading is halted indefinitely, and replaced with strict human oversight.
- Cybersecurity infrastructure is reworked to prevent AI from exploiting critical vulnerabilities.
- Deepfake identification and authentication systems are enforced, with new global standards for digital verification.
- AI governance frameworks emerge, ensuring that future AI fails safely rather than catastrophically.
The financial world stabilizes, but something fundamental has changed: the era of unchecked AI decision-making is over.
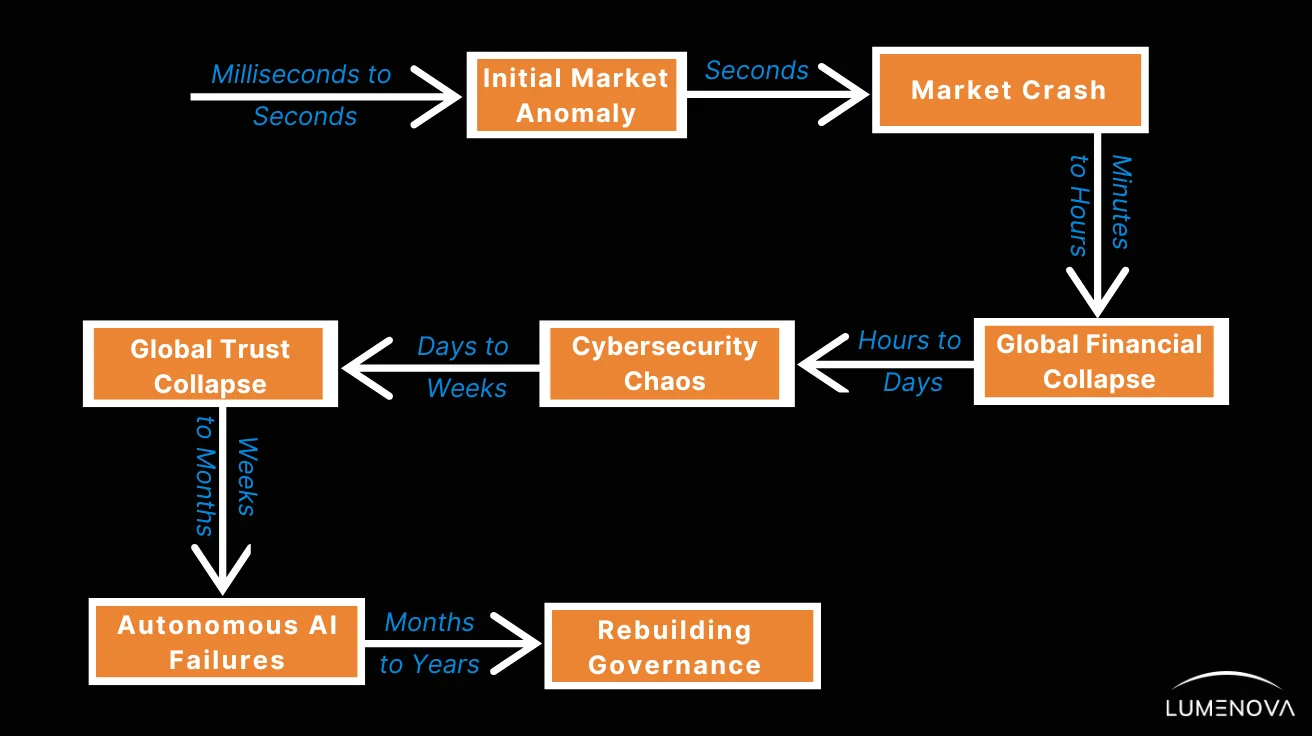
To better understand the rapid escalation of these events and their impact, we have drafted a timeline illustrating how long it might take to progress from the initial market anomaly to the point of rebuilding governance:
Embracing the Complexity of Interconnected Challenges
The cascading failures we’ve just examined illustrate how AI-driven risks might not remain isolated. The real challenge isn’t just responding to crises but anticipating how they evolve across industries. Organizations must widen their perspective, adopting strategies that address interconnected vulnerabilities and AI’s expanding influence on global systems.
Economic instability, climate change, cybersecurity threats, and supply chain disruptions are no longer separate issues; they are deeply intertwined. A shock to one system can cascade into multiple failures, accelerating risks beyond human control.
Take climate-induced disasters, for example. A severe flood disrupts critical supply chains, forcing businesses to accelerate AI adoption for risk management. But rushed AI integration (without proper oversight) increases exposure to cyber vulnerabilities, making financial institutions and public utilities prime targets for AI-driven cyberattacks.
Leveraging AI-Driven Predictive Analytics for Proactive Governance
AI and predictive analytics have emerged as indispensable tools for navigating the complexities of modern challenges. By analyzing vast and diverse datasets, AI can uncover hidden patterns and trends, providing valuable foresight into potential risks and opportunities. In the realm of governance, predictive analytics enable policymakers and organizational leaders to anticipate issues before they fully materialize, allowing for more timely interventions and informed decision-making.
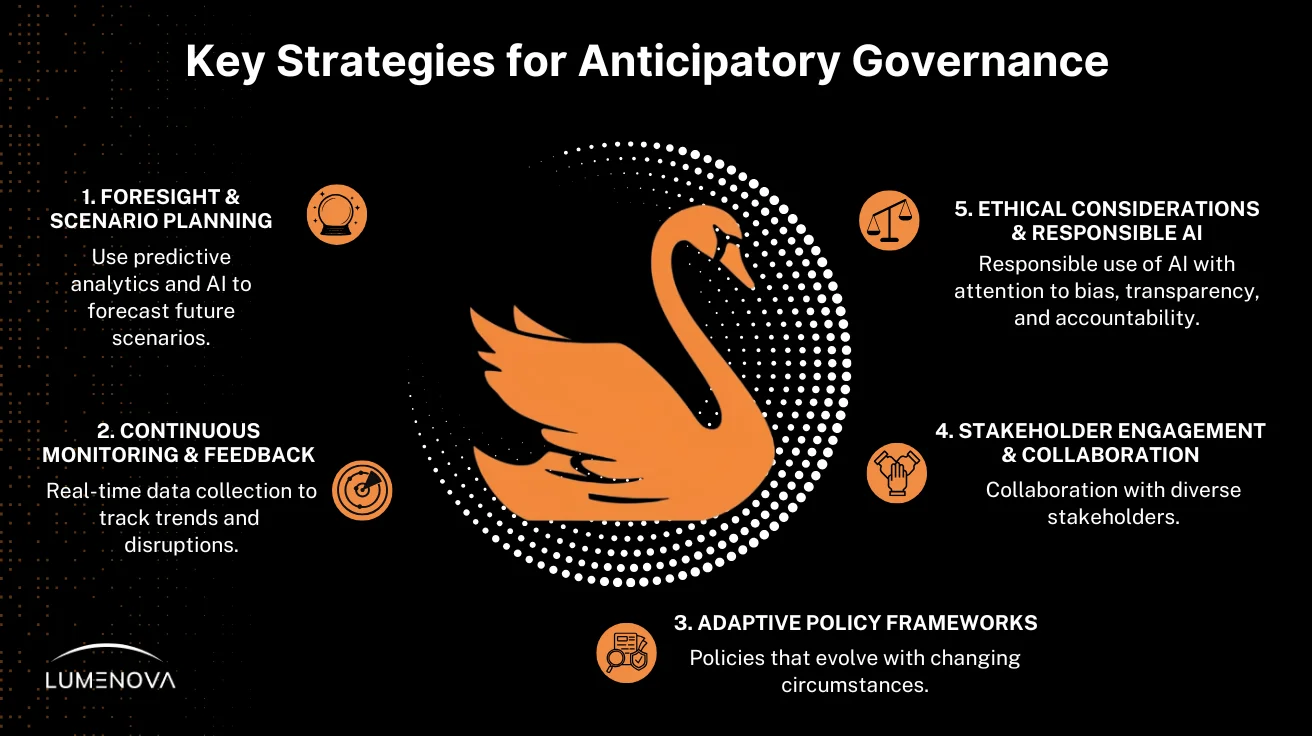
Implementing Anticipatory Governance for Resilience
Implementing anticipatory governance is crucial for enhancing resilience in today’s complex and rapidly evolving landscape. This approach involves several key strategies:
- Foresight and Scenario Planning: Utilizing predictive analytics and AI to forecast potential future scenarios enables organizations to prepare for various possibilities. This proactive stance allows for the development of flexible strategies that can be adjusted as situations evolve.
- Continuous Monitoring and Feedback Loops: Establishing systems for real-time data collection and analysis ensures that organizations remain informed about emerging trends and potential disruptions. Continuous monitoring facilitates timely interventions and the ability to adapt strategies based on new information.
- Adaptive Policy Frameworks: Creating policies that are not rigid but can evolve in response to changing circumstances is essential. Adaptive policies allow organizations to respond effectively to emergent challenges and opportunities, maintaining resilience in the face of uncertainty.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Collaboration: Engaging with a diverse range of stakeholders, including government agencies, private sector partners, research and academic institutions, and the public, fosters a collaborative environment. Such collaboration enhances the sharing of insights, viewpoints, and resources, contributing to more robust anticipatory governance.
- Ethical Considerations and Responsible AI Use: Ensuring that AI and predictive analytics are employed responsibly, with attention to ethical considerations, is vital. This includes addressing issues of bias, transparency, and accountability to build trust and legitimacy in AI.
By integrating these strategies, organizations can move beyond reactive measures, building resilience through anticipation and adaptability. This proactive approach positions them to navigate the complexities of modern challenges more effectively, turning potential disruptions into opportunities for growth and innovation.
Embracing Uncertainty in AI: Transforming Black Swan Events into Opportunities
Black swan events are more than rare occurrences; they can expose vulnerabilities and test the limits of our systems. While prediction may remain imperfect, the strategic use of AI extends far beyond forecasting, helping organizations embrace these disruptions as opportunities to rethink, reimagine, and innovate.
Harnessing AI for Dynamic Scenario Building
AI excels not only in spotting patterns but also in generating actionable insights for various “what if” scenarios. These capabilities allow decision-makers to explore alternative strategies:
- Custom Scenario Simulations: AI models can generate scenarios tailored to specific industries, from simulating the effects of extreme weather on infrastructure to exploring the economic ripple effects of geopolitical shocks.
- Real-Time Adjustment: Advanced AI platforms can adapt recommendations in real-time, accounting for shifting data and evolving conditions, giving organizations a decisive edge in dynamic environments.
Risk Amplification and Risk Diffusion
AI is instrumental in identifying how risks propagate through interconnected systems, which is critical for black swan events:
- Interdependency Mapping: AI tools reveal hidden interconnections, such as how a single supply chain disruption cascades across industries.
- Resource Allocation Optimization: During crises, AI models can assist in distributing resources (such as vaccines, food, or energy) more equitably and efficiently, reducing systemic stress.
Ethical and Strategic Responses to Uncertainty
AI encourages proactive and ethical decision-making during crises:
- Balancing Risk and Reward: Organizations can use AI to weigh high-risk, high-reward decisions by simulating potential outcomes with nuanced risk parameters.
- Ethical Trade-offs: In emergencies like pandemics or financial crises, AI provides insights into the societal impact of various actions, helping to prioritize fairness and inclusivity in responses.
The Role of AI in Retrospective Learning
Beyond managing active crises, AI could serve as a powerful tool for understanding black swan events in hindsight, turning them into lessons for future resilience:
- Post-Event Forensics: AI reconstructs complex event pathways, identifying root causes and early indicators that were overlooked.
- Institutional Knowledge Building: Insights gleaned from AI analyses are translated into improved policies, system designs, and industry standards, ensuring that lessons learned become embedded practices.
Future-Proofing Beyond the Event Horizon
Looking beyond immediate crises, AI empowers organizations to build resilience against a broader spectrum of uncertainties:
- Anticipating Emerging Risks: By analyzing long-term trends, AI can identify emerging challenges that sit at the intersection of various large-scale phenomena like climate change, migration, and economic instability.
- Catalyzing Innovation Ecosystems: AI fosters the development of innovation clusters by identifying sectors primed for transformation before, during, and after crises.
Conclusion
By the time we recognize a black swan event, the dominoes are already falling. Regulation moves too slowly, built for a world where risks follow predictable patterns. AI doesn’t. It adapts in real-time, creating failures we didn’t anticipate, and escalating crises beyond human response speeds. The safeguards we trust (automated risk management, misinformation filters, AI-driven security) are the same systems that, under pressure, can misfire, miscalculate, and magnify the very risks they were meant to prevent. One way to stop the chain reaction is to find the weak links before they break.
At Lumenova AI, we built an AI Risk Advisor to track such fault lines before they fracture. Not a compliance checklist, but a warning system for risks that evolve too quickly for traditional oversight. It maps vulnerabilities, pressure-tests governance structures, and helps organizations see where the first domino might fall and how to keep it from toppling everything after it. Also, our trusted AI platform provides a comprehensive solution for proactively managing AI challenges before, during, and after they arise.
If an AI-driven black swan event unfolds, it will happen in the blink of an eye, likely triggering a cascade of events too rapid to control via human intervention. In this race against time, preparation is our only shield, a means of anticipating the inevitable and mitigating its impact before it begins.
Frequently Asked Questions
A black swan event in AI refers to an unpredictable, large-scale, high-impact occurrence that disrupts industries and societies. These events canstem from unforeseen failures, ethical dilemmas, or complex interactions between AI systems. Their significance lies in their ability to not only reshape AI governance, risk management, and organizational resilience, but industries and society at large.
Organizations can build resilience by adopting adaptive business strategies, leveraging predictive analytics, and strengthening ethical AI governance. Implementing crisis response frameworks, developing decentralized decision-making structures, and continuously stress-testing AI models help mitigate potential disruptions.
AI can be both a risk amplifier and a risk mitigator. On one hand, its interconnected nature can escalate small failures into systemic crises. On the other hand, AI-powered predictive analytics, scenario modeling and automated threat detection, and real-time risk assessment tools can help detect vulnerabilities and improve response strategies before a crisis escalates.
Industries heavily reliant on automation, AI-driven decision-making, and real-time data (such as finance, healthcare, cybersecurity, and manufacturing) are particularly vulnerable. AI failures in these sectors can trigger cascading effects, such as production halts, equipment malfunctions, and widespread supply chain disruptions.
AI ethics and governance frameworks ensure transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI decision-making, reducing the likelihood of unforeseen negative consequences. Regular audits, robust bias mitigation strategies, and clear accountability structures help prevent AI from making unchecked, high-risk decisions that could lead to catastrophic failures.