
Contents
A Deloitte study highlights the need to rethink our approach to Artificial Intelligence (AI). While mere “trust” in AI is insufficient, a strong framework for AI governance, coupled with effective risk management strategies, can pave the way for its successful integration. Simply “synchronizing” people, processes, and technology is inadequate. Therefore, a seamless and collaborative environment is mandatory.
Generative AI, though possessing transformative potential across various industries, also introduces unforeseen challenges. Therefore, these obstacles necessitate a proactive approach, demanding careful consideration and mitigation strategies.
Understanding Responsible AI
Defining Responsible AI
Just like we mentioned above, responsible AI principles guide the design, development, deployment, and use of AI. This approach is imperative for building trust in AI solutions, which have the potential to empower organizations and their stakeholders. According to IBM, human-centric AI goes beyond that, involving the consideration of a broader societal impact of AI systems. In essence, it aims to ensure that AI is developed and used ethically, transparently, and in a way that benefits everyone.
Importantly, responsible AI is not just about the technology itself but also about the people and processes involved in its development and use. To achieve this, it requires a multidisciplinary approach that involves experts from various fields, including ethics, law, policy, and social sciences. Furthermore, it necessitates collaboration between different stakeholders such as businesses, governments, and civil society organizations.
The Importance of Responsible AI in the Generative AI Era

- Untapped Potential, Mitigated Risks: Generative AI holds immense potential to revolutionize industries, but comes with challenges like cybersecurity, privacy, and bias. Therefore, the responsible practices act as a framework to manage these risks and unlock the full potential of gen AI.
- Building Trust Across AI: Responsible AI should be seen as more than just patching up errors. It’s about building trust in everything AI does. That means making sure AI is developed ethically, performs flawlessly, and minimizes any potential risks.
- Beyond Tech, Societal Impact: The real power of Responsible AI? Well, its purpose is to make sure everyone gets a slice of the AI pie, not just the lucky few. It tackles it all – protecting people’s privacy, ensuring fairness, and considering how AI impacts society as a whole.
- Holistic Approach for All AI: It takes a holistic approach, considering the bigger picture of how AI affects society and ethics. This ensures responsible development and implementation across all AI projects, not just one or two.
Generative AI Capabilities and Limitations
What Generative AI Can Do
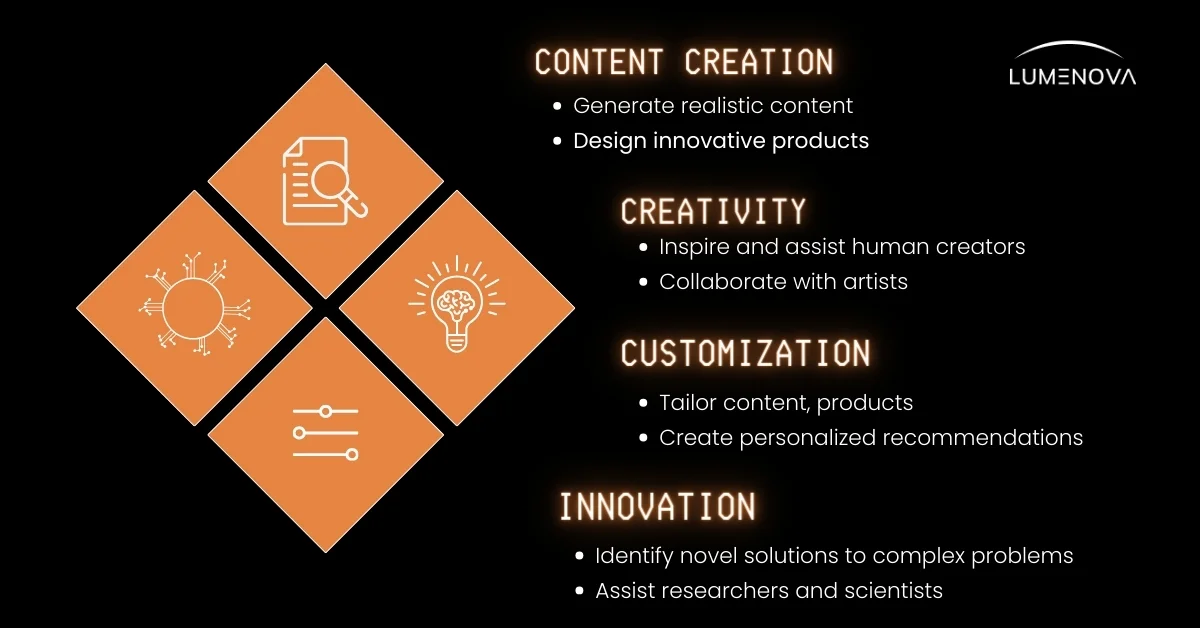
One of the most exciting aspects of generative AI is its ability to create realistic and engaging content. By leveraging cutting-edge deep learning techniques and vast amounts of data, generative AI can produce images, videos, and animations that are virtually indistinguishable from those created by humans. Moreover, it can generate personalized text content, such as articles and product descriptions, tailored to individual preferences and needs. This capability has far-reaching implications for industries like marketing, journalism, and entertainment, where compelling content is essential for capturing and retaining audience attention.
Furthermore, generative AI can serve as a powerful tool for enhancing creativity and innovation. By providing novel ideas and concepts, it can inspire and assist human creators in exploring new creative directions. Collaborating with artists, designers, and writers, generative AI can streamline the creative process, automating repetitive tasks and generating variations on themes. This not only saves time and effort but also enables individuals with limited artistic skills to express their ideas visually or through other media.
In addition to content creation and creativity, generative AI excels in personalization and customization. By analyzing user preferences and behavior, it can tailor content, products, and experiences to individual needs, creating a more engaging and satisfying user experience. From personalized product recommendations to customized designs and optimized user interfaces, generative AI has the potential to revolutionize the way businesses interact with their customers.
Lastly, generative AI can be a valuable asset in problem-solving and innovation. By exploring vast design spaces and combinations, it can identify novel solutions to complex problems that might elude human experts. In research and scientific contexts, generative AI can assist in generating hypotheses and testing ideas, accelerating the discovery process. Moreover, it can optimize processes and systems by generating and evaluating multiple scenarios and alternatives, facilitating rapid prototyping and experimentation.
Recent studies have showcased the transformative potential of generative AI across various domains. For instance, a study conducted by researchers at OpenAI demonstrated how generative AI can create photorealistic images and videos from textual descriptions, opening up new possibilities for content creation and storytelling. Similarly, a study by Google Brain researchers highlighted the ability of generative AI to design optimized machine learning architectures, potentially accelerating the development of AI systems.
Recognizing Generative AI Limitations
Despite its many advantages, generative AI also has some limitations. One of the main limitations is that generative AI can only create content based on the data it has been trained on. This means that if the training data is biased or incomplete, the generative AI system will produce biased or incomplete content.
Another limitation of generative AI is that it can be difficult to control the output. Unlike traditional software, which follows a set of rules and instructions, generative AI systems are designed to be creative and unpredictable. This means that it can be difficult to predict what the system will create, and it can be difficult to control the output once it has been created.
Finally, generative AI can be expensive to develop and maintain. Developing a generative AI system requires a large amount of data and computing power, which can be expensive to acquire and maintain. Additionally, generative AI systems require ongoing maintenance and updates to ensure that they continue to produce high-quality output.
Risks and Challenges of Generative AI
Generative AI is a powerful tool that allows businesses to create content quickly and at a low cost. However, its adoption comes with a degree of risk that organizations must address to ensure responsible use of generative AI. Below, we’ll examine some challenges and risks associated with it.
Cyber and Privacy Risks
One of the primary risks associated with generative AI is cyber and privacy risks. As generative AI technology continues to advance, it becomes easier for cybercriminals to create deepfakes, which can be used to spread disinformation, commit fraud, and damage reputations. Organizations must prioritize the responsible use of generative AI to mitigate these risks. This includes implementing strong security measures to protect against cyber threats and ensuring that data privacy is maintained at all times.
Ethical and Bias Considerations
Another significant challenge of generative AI is ethical and bias considerations. Generative AI algorithms learn from the data they are trained on, which means that if the data is biased, the algorithm will be biased too. This can lead to unintended consequences, such as perpetuating stereotypes or discriminating against certain groups of people. To address these challenges, organizations must ensure that their generative AI models are trained on diverse and unbiased data sets. They should also implement ethical guidelines to ensure that the AI is being used responsibly.
Intellectual Property Concerns
Generative AI can also expose organizations to intellectual property concerns. Since AI can create content quickly and at a low cost, it can be used to create counterfeit products, infringe on patents, and steal trade secrets. To mitigate these risks, organizations must ensure that their generative AI models are not infringing on any existing intellectual property rights. They should also implement very strong IP protection strategies to safeguard their own intellectual property.
Transparency and Explainability
These aspects are very important for understanding how algorithms work, enabling a deeper evaluation of the reliability of results and the identification of potential flaws or biases. Beyond that, ensuring transparency and explainability in generative AI systems can further mitigate intellectual property risks. Moreover, they can contribute to building trust in AI technologies, facilitating their adoption across a wider range of applications and improving collaboration between humans and machines.
Building Trust with Responsible AI
Building trust with AI is indispensable for businesses to fully harness the power of generative AI. However, there are several challenges that must be addressed to establish trust in artificial intelligence.
Trust Challenges in AI
AI holds immense promise, but trust remains a hurdle. Two key challenges hinder its adoption:
- Potential for Bias: AI reflects the biases present in its training data. Biased data leads to biased AI, which can perpetuate unfairness.
- Lack of Transparency: Many AI systems are “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand their decision-making process. This hinders our ability to assess their trustworthiness.
The Role of Responsible AI in Trust
Responsible use of AI can help address these challenges and build trust in artificial intelligence. It involves designing, developing, and deploying AI systems with the goal of minimizing risks and maximizing benefits.
One way to achieve responsible AI is to ensure that AI systems are transparent and explainable. This means that users can understand how the AI system arrives at a certain decision.
Additionally, responsible AI involves ensuring that AI systems are fair and unbiased. This can be achieved by using diverse and representative data sets to train AI systems.
Another important aspect of responsible AI is ensuring that AI systems are secure and protect user privacy. This involves implementing security measures to prevent unauthorized access to data and ensuring that user data is used only for its intended purpose.
Additionally, responsible AI involves ensuring that AI systems are respectful of intellectual property. In order to mitigate bias and reduce the risk of copyright content, AI systems should be trained on diverse and representative datasets.
Implementing Responsible AI
To ensure that your AI system is responsible, you need to follow certain principles and use frameworks and templates to guide its implementation. You also need to manage the AI life cycle effectively to ensure that it meets the necessary standards.
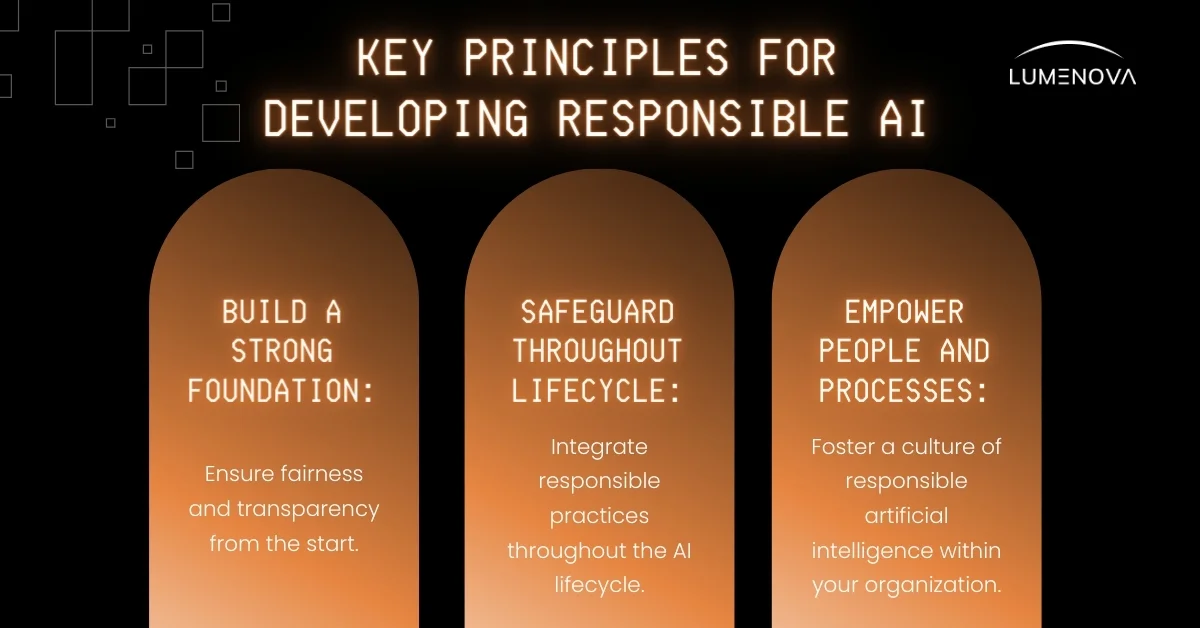
Frameworks and Templates
To harness the power of AI responsibly, organizations must prioritize compliance, risk management, and ethical governance. This is where established frameworks and standards become invaluable tools.
Integrating frameworks like the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, the EU Artificial Intelligence Act, and the ICO – AI and Data Protection Risk Toolkit, along with international standards like ISO/IEC 42001, can provide a solid foundation for your AI governance strategy. These resources, along with emerging regional regulations like those in Colorado and California, offer guidance on:
- compliance
- risk mitigation
- ethical practices
While the landscape of AI governance may seem daunting, embracing these frameworks and standards is a critical step towards building a responsible AI culture within your organization. As a result, Lumenova provides the tools and guidance you need to unlock the full potential of AI while fostering trust and transparency. Let’s work together to build a future of equitable AI applications.
AI Life Cycle Management
- Data collection: Ensure that your data is diverse and representative of the population you are serving. Also, ensure that your data is accurate and up-to-date.
- Testing: You should conduct a comprehensive evaluation and testing program to solidify the accuracy, fairness, and security of generative AI models throughout their entire lifecycle. This program actively exposes vulnerabilities through adversarial and red team testing, simulating real-world threats. Proactive identification of weaknesses allows you to fortify the model against misuse and guarantee its power and reliability.
- Deployment: Deploy it in a controlled environment to ensure that it is safe and secure. At the same time, ensure that your model is accessible to everyone who needs it.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor the model to ensure that it is performing as expected. It oversees the entire journey of an AI model, ensuring responsible development and use. AI Life Cycle Management involves human oversight throughout the process, including setting goals, monitoring performance, and incorporating feedback for better, more ethical AI.
Responsible AI at the Organizational Level
Implementing responsible AI usage at the organizational level requires a comprehensive approach that involves executive responsibilities, policy, and responsible AI governance. This ensures that artificial intelligence is developed and deployed in an ethical, transparent, and trustworthy manner.
Executive Responsibilities
The executive leadership of an organization plays a critical role in ensuring that AI is used responsibly. They must understand the potential risks and benefits of AI and ensure that the organization’s AI strategy aligns with its values and goals. This involves:
- Establishing a culture of responsible AI within the organization
- Providing resources and support for responsible AI initiatives
- Ensuring that AI is developed and deployed in an ethical and transparent manner
- Regularly reviewing and updating AI policies and procedures
Policy and Governance
Policy and governance frameworks are also very essential for ensuring that AI is developed and deployed in a responsible and ethical manner. These frameworks should be designed to address the following:
- Data privacy and security
- Bias and fairness
- Transparency and explainability
- Accountability and oversight
To ensure that these policies are effective, organizations should consider the following:
- Establishing an AI ethics committee or board to oversee AI development and deployment
- Conducting regular audits and assessments of AI systems to identify and address potential issues
- Providing training and resources to employees to ensure that they understand the ethical implications of AI
Conclusion
Building trust in AI is imperative to maximizing its positive impact. Challenges like bias and transparency can create roadblocks, but fortunately, responsible AI principles pave the way for ethical and empowering AI development. By proactively managing AI risks, organizations can cultivate confidence in these solutions and ensure they contribute meaningfully to society.
Now, how can you unlock the power of fair AI & how to use it responsibly? At Lumenova AI — we streamline and automate the process, empowering you to build trust in your AI solutions with greater efficiency. Book your demo to explore how our ideas can help you navigate responsible AI development and harness the full potential of trustworthy & responsible AI.
Frequently Asked Questions
Responsible AI refers to the ethical design, development, and deployment of AI systems to ensure fairness, transparency, accountability, security, and safety. In the Generative AI era, it is crucial for mitigating risks such as bias, misinformation, and privacy violations while maximizing AI’s potential benefits at scale.
Generative AI poses risks like cybersecurity threats, biased outputs, privacy violations, intellectual property concerns, and the spread of misinformation. Addressing these challenges requires robust governance frameworks, transparency, and risk mitigation strategies.
Organizations can build trust by implementing Responsible AI principles and best practices, ensuring transparency in AI decision-making, conducting bias audits, maintaining human oversight, and adhering to ethical AI governance and risk management frameworks such as the NIST AI RMF and EU AI Act.
AI life cycle management ensures that AI models are developed, tested, deployed, and monitored responsibly. This includes collecting diverse and unbiased data, conducting rigorous performance testing and adversarial evaluations, implementing robust security measures, and continuously monitoring AI for fairness and reliability.
Lumenova AI provides tools and expertise to help organizations implement Responsible AI, automate risk management, and ensure compliance with ethical AI standards. Our platform streamlines AI governance, bias detection, and transparency measures, fostering trust in AI-driven solutions.