
Contents
A modified version of this article was originally published on Spiceworks.
The ascent of generative AI has been remarkable in recent years, and its growth shows no signs of slowing down. We’ve all heard about the various generative AI models like ChatGPT, Dall-E, Midjourney, and StableDiffusion, and perhaps even had the chance to try them out.
To provide an introduction, let’s define generative AI as artificial intelligence algorithms that have the ability to produce content that is virtually indistinguishable from content created by humans. This content can include images, videos, audio, text, and other forms of media, and is often referred to as synthetic media.
Generative AI has a wide range of applications due to its capacity to generate high-quality content with minimal effort. It can be used for content creation, data augmentation, chatbots, virtual assistants, and other creative purposes.
This type of AI has the potential to revolutionize content creation and our interaction with it. The past few months have provided ample evidence of this as ChatGPT has reshaped our understanding of real-time content creation.
Let’s delve into the rise of ChatGPT
In November 2022, OpenAI introduced ChatGPT, an AI bot built on OpenAI’s GPT-3 series of large language models. Despite being in its early stages, the prototype quickly garnered public attention for its comprehensive answers across various domains of knowledge. What happened next was remarkable.
Within the first five days of its release, over 1 million people logged into the platform to test ChatGPT’s capabilities. The public’s reliance on ChatGPT grew rapidly, extending to blog posts, social media content, poetry, and even code generation. Four months later, OpenAI’s valuation skyrocketed to an estimated $29 billion in 2023.
Today, it’s evident that ChatGPT is not only sought after by marketers and content creators worldwide but also by programmers and data scientists. While ChatGPT cannot write complete programs or scripts, it can assist programmers with tasks such as debugging, code refactoring, and generating code snippets.
For example, ChatGPT can explain and rectify errors in code snippets, making it a valuable tool. Take a look:
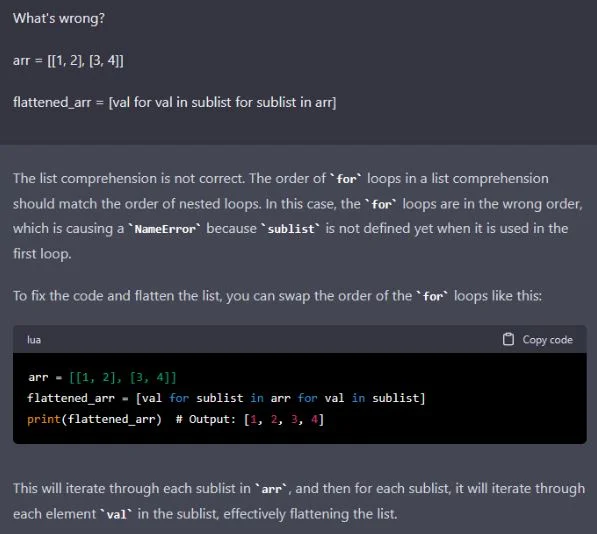
Additionally, ChatGPT can provide general programming guidance, including best practices like code commenting, proper data type usage, and error handling.
Data scientists and machine learning engineers also find ChatGPT to be a helpful assistant. It can aid in tasks such as data cleaning, feature engineering, model selection, hyperparameter tuning, and data augmentation.
Now, let’s discuss the risks and benefits associated with generative AI, including ChatGPT.
Striking a Balance: Examining the Risks and Benefits of Generative AI
Generative AI has undoubtedly demonstrated numerous benefits that have propelled its adoption across various industries. The recent surge in its popularity highlights its potential to empower users in unprecedented ways.
However, it is important to approach generative AI with a balanced perspective, considering both its advantages and potential risks. While the benefits are undeniable, it is crucial to be mindful of the potential hazards associated with third-party solutions such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Stability AI’s StableDiffusion.
Let’s delve deeper into these considerations.
Risk 1: Intellectual property theft & confidentiality breaches
Generative AI produces output based on learned patterns from input data. This can lead to disputes over authorship and ownership of generated content, potentially resulting in allegations of plagiarism or copyright infringement. Companies must carefully balance the benefits of generative AI with the associated risks.
Concerns over the inclusion or resemblance of confidential information have prompted companies like Amazon, Microsoft, and Walmart to caution against sharing code with ChatGPT.
When using such models, it’s always recommended to pay attention to the small print and being wary of using any sensitive information provided by clients, customers, or partners in the input prompts, especially if this data falls under confidentiality agreements.
Risk 2: Deceptive trade practices
A recent survey conducted by Fishbowl revealed that a significant number of employees from various companies, including Amazon, Google, and Twitter, use ChatGPT for work without informing their supervisors. While outsourcing certain work-related tasks to ChatGPT may seem appealing, it can lead to unethical or even illegal practices.
Using deceptive practices, including impersonating humans, is prohibited by federal laws like the FTC Act.
To promote responsible practices for synthetic media, industry leaders such as OpenAI, Adobe, BBC, TikTok, and Bumble have joined forces to support the implementation of frameworks and guidelines.
Initiatives like Partnership on AI collaborate with global institutions to establish responsible use guidelines for synthetic media.
Risk 3: Inaccurate results & bias propagation
Generative AI does not inherently discern truth from falsehood, and answers from ChatGPT can be open to interpretation. Skepticism and reliable fact-checking are essential when using generative AI models.
Inaccurate statements can harm an organization’s reputation, as seen in cases where AI-written articles contained errors or when AI bots generated nonsensical or biased outputs.
- CNET was scrutinized because errors were found in more than half of their AI-written articles.
- Meta’s AI bot Galactica was heavily criticized and ultimately pulled back for generating what experts called ‘statistical nonsense’ and ‘deep scientific fakes’.
- Even the public’s latest favorite – ChatGPT – got its little Internet corner dedicated to failures and bizarre behavior.
Generative AI can also perpetuate or amplify existing biases present in the training data. Despite efforts to mitigate bias, there is no silver bullet, particularly for black-box generative AI models.
Instances of ChatGPT exhibiting prejudice or inappropriate responses have been observed, highlighting the need for cautious usage to prevent unjust treatment or discrimination.
- ChatGPT showed instances of sexism or racism in this viral Tweet.
- It also told some users that it would be okay to torture people from some minority backgrounds, as shown in this example.
Regulators worldwide stress the importance of responsible AI use, and initiatives like NIST’s AI Risk Management Framework provide guidance for trustworthy AI systems. The European Union is also working towards regulating generative AI under the EU AI Act.
Risk 4: Malicious & abusive content
Generative AI, including ChatGPT, can also be exploited for malicious purposes. Cybercriminals can enhance phishing attempts and social engineering scams using ChatGPT to generate convincing emails. Therefore, organizations need to strengthen cybersecurity measures and educate employees about potential risks.
Furthermore, the coding capabilities of ChatGPT can empower malicious actors to create malware or ransomware. Although models like ChatGPT aim to block such malicious use, bad actors may find workarounds.
Additionally, generative AI makes it easier to create deep fakes, which can be used to spread false information, propaganda, or tarnish the reputation of individuals or organizations.
Given the potential impact of disinformation, organizations must proactively monitor their brands and be prepared to respond during crises.
Risk 5: Building and deploying biased and unsafe ML models
The accessibility of generative AI to non-experts may also allow users without a background in computer science or data analytics to experiment with machine learning (ML) models.
Here is an example provided by ChatGPT when asked to build a linear regression model in Python:
This is a very simple example. However, ChatGPT can help generate code for more complex models, preprocessing steps, and evaluation metrics. It can also be used to explore various hyperparameters, compare different models, and debug issues.
While this provides opportunities, it also introduces risks. Inexperienced users may lack an understanding of the complexities involved in developing and deploying effective models.
Poorly designed or misused ML models can lead to discrimination, bias, safety concerns, and other harmful consequences. As ML models can significantly impact lives, it is crucial to ensure responsible and ethical development practices.
What role does ChatGPT play in your organization? Consider the risks and benefits associated with its use and share your thoughts with us on LinkedIn or Twitter.
Frequently Asked Questions
Generative AI poses risks such as the potential misuse in deepfake creation, the spread of misinformation, and the reinforcement of biases in training data. Additionally, concerns exist around data privacy, AI security, and the ethical implications of AI-generated content.
Generative AI enhances business efficiency by automating content creation, improving design and marketing, and delivering personalized customer experiences. It also supports data analysis, generating insights that drive strategic decision-making.
Ethical concerns include ensuring AI transparency, addressing algorithmic bias, protecting intellectual property rights, and maintaining user privacy. Establishing AI governance frameworks and adhering to AI regulations are essential for responsible AI deployment.
While generative AI can automate certain tasks, it also creates new roles in AI development, oversight, and creative collaboration. The overall employment impact depends on industry adaptation, with upskilling and reskilling playing a key role in workforce transformation.
To reduce risks, users should critically evaluate AI-generated content, verify sources, and use AI tools responsibly. Staying informed about AI regulations and ethical best practices helps ensure safe and accountable AI usage.